Hair Transplant
A hair transplant is a surgery that moves hair to bald or thinning areas of the scalp. Also called hair restoration or hair replacement. Dermatologists (healthcare providers specializing in the skin) or plastic surgeons (healthcare providers specializing in cosmetic and reconstructive procedures) perform hair transplants.
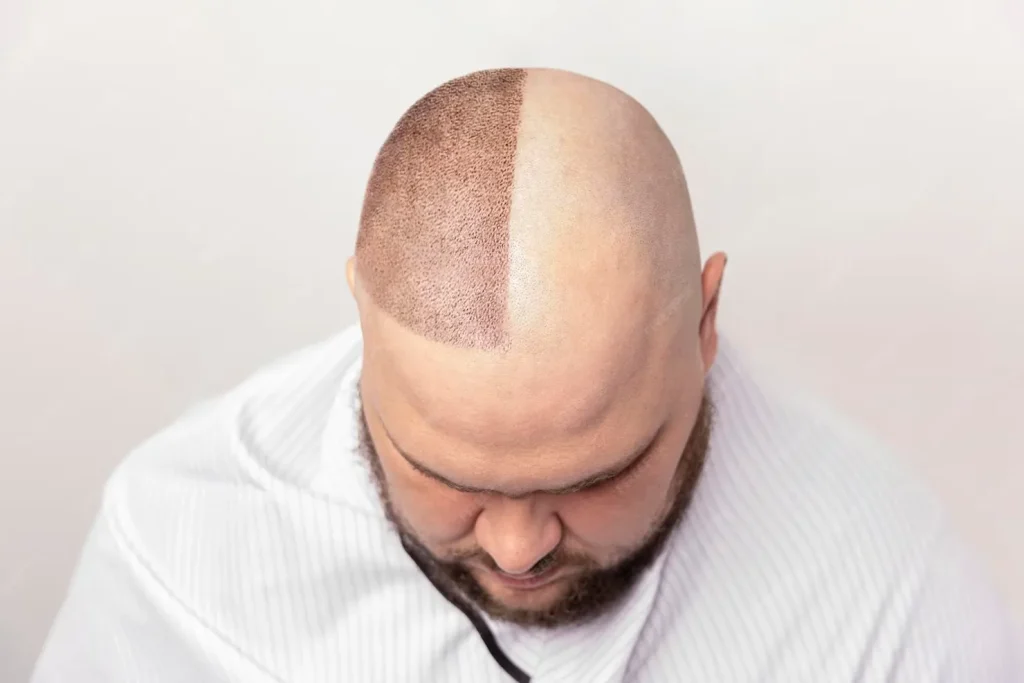

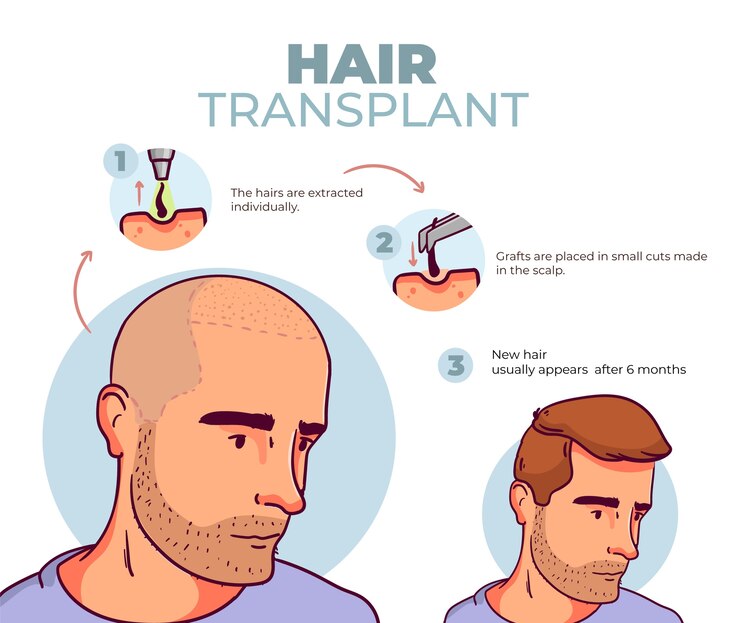
How does a hair transplant work?
The healthcare provider takes grafts, or small pieces of skin, from areas of the body that contain healthy hair. This area is called the donor site. It’s usually on your head, at the back of your scalp where hair tends to be thickest and least affected by the ageing process. The healthcare provider moves the grafts to hairless parts of the scalp. Once the transplanted skin heals, it should continue to grow hair.
Ideal Candidate for Liposuction
Because liposuction is not a weight loss method, the ideal candidate for liposuction is in relatively good shape and around their ideal body weight. Even despite regular exercise, candidates for liposuction can experience stubborn pockets that won’t budge. If you are looking to maintain soft, even curves after liposuction, visit Dr. Amey Pednekar for one of the best Goa can offer you.
In addition to the above, liposuction candidates should have good skin elasticity, which will allow it to conform to the new, slimmer contours. If this is not the case, liposuction will not only produce zero improvement, but it will also make you look worse, as the fat underneath the skin is what’s holding the skin tight. When the fat is removed, semi-loose skin will become very loose skin. This is a condition very common to moms and anyone who has undergone significant weight loss.
Candidacy for liposuction is best discovered in a live consultation, at which time Dr. Amey can examine your trouble areas and determine which cosmetic treatment is most suitable. Additionally, Dr. Amey will examine the quality of your skin to determine its elasticity. In this way, he will ensure you won’t be left with contour irregularities following liposuction.
Have a Question ?
Reach out to know more details about the treatment.
Benefits
Liposuction is normally done for cosmetic purposes, but it is sometimes used to treat certain conditions.
These include:
- Gynecomastia: fat accumulation under a male breasts.
- Lipodystrophy syndrome: Fat accumulates in one part of the body and is lost in another. Liposuction can improve the patient’s appearance by providing a more natural looking body fat distribution.
- Lipomas: These are benign, fatty tumors
Liposuction in Mommy Makeover :
Mothers, after having children, almost always have some degree of looseness to their skin, making them poor candidates for liposuction.
All too often, people try to “get away with” liposuction in lieu of excisional surgery such as a tummy tuck post pregnancy. In many cases, they are only left disappointed down the line when not only do they not look better, they look worse than they ever did. Common problems are loose skin and indentations and deformities known as contour irregularities.
Results
After liposuction, swelling typically subsides within a few weeks. It is important to be wearing the prescribed pressure garment during this period to ensure maximum benefits from the surgery and decrease the charges of hematoma formation. In a matter of 4 weeks, the treated area should look less bulky. Within several months, expect the treated area to have a leaner appearance.
