Acne Treatment in Goa
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when your hair follicles become plugged with oil and dead skin cells. It causes whiteheads, blackheads or pimples. Acne is most common among teenagers, though it affects people of all ages.
Effective acne treatments are available, but acne can be persistent. The pimples and bumps heal slowly, and when one begins to go away, others seem to crop up
Effective acne treatments are available, but acne can be persistent. The pimples and bumps heal slowly, and when one begins to go away, others seem to crop up.
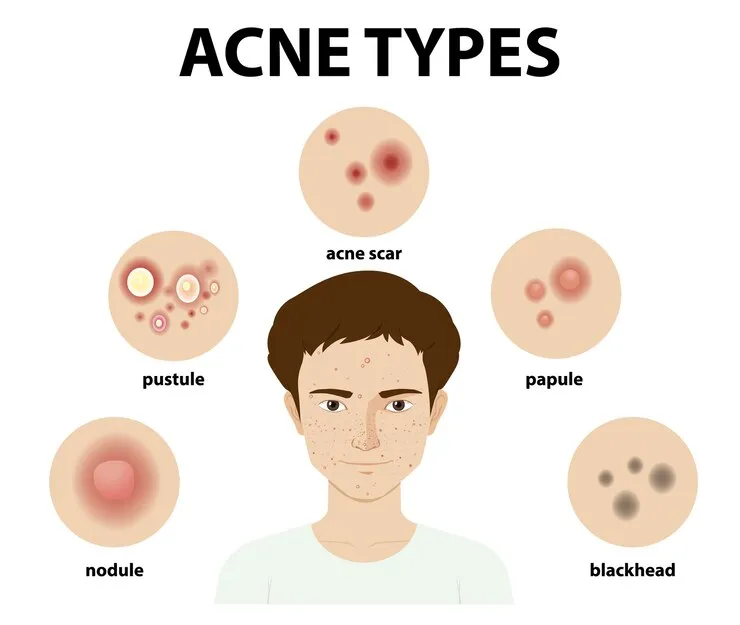
Acne Type:
- Whiteheads (closed plugged pores)
- Blackheads (open plugged pores)
- Small red, tender bumps (papules
- Pimples (pustules), which are papules with pus at their tips
- Large, solid, painful lumps under the skin (nodules)
- Painful, pus-filled lumps under the skin (cystic lesions)
When to see a doctor
If self-care remedies don’t clear your acne, see your primary care doctor. He or she can prescribe stronger medications. If acne persists or is severe, you may want to seek medical treatment from a doctor who specializes in the skin (dermatologist or pediatric dermatologist).
For many women, acne can persist for decades, with flares common a week before menstruation. This type of acne tends to clear up without treatment in women who use contraceptives.
In older adults, a sudden onset of severe acne may signal an underlying disease requiring medical attention.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warns that some popular nonprescription acne lotions, cleansers and other skin products can cause a serious reaction. This type of reaction is quite rare, so don’t confuse it with any redness, irritation or itchiness that occurs in areas where you’ve applied medications or products.
Seek emergency medical help if after using a skin product you experience:
- Faintness
- Swelling of the eyes, face, lips or tongue
- Tightness of the throat
- Difficulty breathing
Have a Question ?
Reach out to know more details about the treatment.
Causes
How acne develops
Acne typically appears on your face, forehead, chest, upper back and shoulders because these areas of skin have the most oil (sebaceous) glands. Hair follicles are connected to oil glands.
The follicle wall may bulge and produce a whitehead. Or the plug may be open to the surface and darken, causing a blackhead. A blackhead may look like dirt stuck in pores. But actually the pore is congested with bacteria and oil, which turns brown when it’s exposed to the air.
Pimples are raised red spots with a white center that develop when blocked hair follicles become inflamed or infected with bacteria. Blockages and inflammation deep inside hair follicles produce cystlike lumps beneath the surface of your skin. Other pores in your skin, which are the openings of the sweat glands, aren’t usually involved in acne.
Four main factors cause acne:
- Excess oil (sebum) production
- Hair follicles clogged by oil and dead skin cells
- Bacteria
- Inflammation
Acne Myths and Complications
These factors have little effect on acne:
- Chocolate and greasy foods. Eating chocolate or greasy food has little to no effect on acne.
- Hygiene. Acne isn’t caused by dirty skin. In fact, scrubbing the skin too hard or cleansing with harsh soaps or chemicals irritates the skin and can make acne worse.
- Cosmetics. Cosmetics don’t necessarily worsen acne, especially if you use oil-free makeup that doesn’t clog pores (noncomedogenics) and remove makeup regularly. Nonoily cosmetics don’t interfere with the effectiveness of acne drugs.
People with darker skin types are more likely than are people with lighter skin to experience these acne complications:
- Scars. Pitted skin (acne scars) and thick scars (keloids) can remain long-term after acne has healed.
- Skin changes. After acne has cleared, the affected skin may be darker (hyperpigmented) or lighter (hypopigmented) than before the condition occurred.
Risk Factors
- Age. People of all ages can get acne, but it’s most common in teenagers.
- Hormonal changes. Such changes are common during puberty or pregnancy.
- Family history. Genetics plays a role in acne. If both of your parents had acne, you’re likely to develop it too.
- Friction or pressure on your skin. This can be caused by items such as telephones, cellphones, helmets, tight collars and backpacks.
- Greasy or oily substances. You may develop acne where your skin comes into contact with oil or oily lotions and creams.
